1212. Infinite Sequence - 2
Define an infinite sequence A as follows:
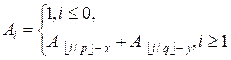
Given the values n, p,
q,
x and y, compute An.
Input. Five integers n, p, q,
x, y (0 £ n £ 1013, 2 £ p, q £ 109, 0 £ x, y £ 109).
Output. Print the value of An.
|
Sample output 1 |
|
|
12 2 3 1 0 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
10000000 2 3 10000000 10000000 |
2 |
SOLUTION
recursion
Algorithm analysis
Since n £ 1013, storing all
values Ai (i = 0, 1, …, n) is impossible,
either using an array or a map structure due to memory limitations.
Therefore, we’ll use recursion
defined by the recurrence relation for computations.
At the same
time, the values Ai for i < 5000000 will be stored in the array m to avoid repeated
computations and speed up
the program.
Algorithm implementation
To store the values Ai (i < 5000000), declare an array m.
#define MAX 5000000
long long m[MAX];
The function f
computes the value of An.
long long calc(long long n, long long p, long long q,
long
long x, long long y)
{
If n £ 0, then An = 1.
if (n <=
0) return 1;
If n < 5000000 and the value
m[n] is already computed (is not zero),
return it.
if ((n < MAX) && m[n] > 0) return m[n];
Perform a recursive computation of An
according to the formula provided in the problem statement.
long long temp = calc(n/p-x,p,q,x,y) +
calc(n/q-y,p,q,x,y);
If n < 5000000, store the
result An in the array m
to avoid repeated computations in the future.
if (n <
MAX) m[n] = temp;
return temp;
}
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %lld",&n,&p,&q,&x,&y);
Compute and print the
answer.
res = calc(n,p,q,x,y);
printf("%lld\n",res);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int MAX = 5000000;
static long m[] = new long[MAX];
public static long f(long n, long p, long q, long x, long y)
{
if (n <= 0) return 1;
if (n < MAX && m[(int)n] > 0) return m[(int)n];
long temp = f(n/p-x,p,q,x,y) + f(n/q-y,p,q,x,y);
if (n < MAX) m[(int)n] = temp;
return temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
long n = con.nextLong();
long p = con.nextLong();
long q = con.nextLong();
long x = con.nextLong();
long y = con.nextLong();
long res = f(n,p,q,x,y);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
To store the values Ai (i < 5000000), declare a list m.
MAX = 5000000
m = [0] * MAX
The function f
computes the value of An.
def f(n, p, q, x,
y):
If n £ 0, then An = 1.
if n <= 0:
return 1
If n < 5000000 and the value
m[n] is already computed (is not zero),
return it.
if n < MAX and m[n]:
return m[n]
Perform a recursive computation of An
according to the formula provided in the problem statement.
temp =
f(n // p - x, p, q, x, y) + f(n // q - y, p, q, x, y)
If n < 5000000, store the
result An in the array m
to avoid repeated computations in the future.
if n < MAX: m[n] = temp
return temp
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
n, p, q, x, y = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the
answer.
res = f(n, p, q, x, y)
print(res)